[et_pb_section bb_built=”1″][et_pb_row][et_pb_column type=”4_4″][et_pb_text _builder_version=”3.26.6″ text_text_align=”justify” text_text_shadow_horizontal_length=”text_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ text_text_shadow_horizontal_length_tablet=”0px” text_text_shadow_vertical_length=”text_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ text_text_shadow_vertical_length_tablet=”0px” text_text_shadow_blur_strength=”text_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ text_text_shadow_blur_strength_tablet=”1px” text_orientation=”justified” link_text_shadow_horizontal_length=”link_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ link_text_shadow_horizontal_length_tablet=”0px” link_text_shadow_vertical_length=”link_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ link_text_shadow_vertical_length_tablet=”0px” link_text_shadow_blur_strength=”link_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ link_text_shadow_blur_strength_tablet=”1px” ul_text_shadow_horizontal_length=”ul_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ ul_text_shadow_horizontal_length_tablet=”0px” ul_text_shadow_vertical_length=”ul_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ ul_text_shadow_vertical_length_tablet=”0px” ul_text_shadow_blur_strength=”ul_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ ul_text_shadow_blur_strength_tablet=”1px” ol_text_shadow_horizontal_length=”ol_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ ol_text_shadow_horizontal_length_tablet=”0px” ol_text_shadow_vertical_length=”ol_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ ol_text_shadow_vertical_length_tablet=”0px” ol_text_shadow_blur_strength=”ol_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ ol_text_shadow_blur_strength_tablet=”1px” quote_text_shadow_horizontal_length=”quote_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ quote_text_shadow_horizontal_length_tablet=”0px” quote_text_shadow_vertical_length=”quote_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ quote_text_shadow_vertical_length_tablet=”0px” quote_text_shadow_blur_strength=”quote_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ quote_text_shadow_blur_strength_tablet=”1px” header_text_align=”justify” header_text_shadow_horizontal_length=”header_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_text_shadow_horizontal_length_tablet=”0px” header_text_shadow_vertical_length=”header_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_text_shadow_vertical_length_tablet=”0px” header_text_shadow_blur_strength=”header_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_text_shadow_blur_strength_tablet=”1px” header_2_text_shadow_horizontal_length=”header_2_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_2_text_shadow_horizontal_length_tablet=”0px” header_2_text_shadow_vertical_length=”header_2_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_2_text_shadow_vertical_length_tablet=”0px” header_2_text_shadow_blur_strength=”header_2_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_2_text_shadow_blur_strength_tablet=”1px” header_3_text_shadow_horizontal_length=”header_3_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_3_text_shadow_horizontal_length_tablet=”0px” header_3_text_shadow_vertical_length=”header_3_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_3_text_shadow_vertical_length_tablet=”0px” header_3_text_shadow_blur_strength=”header_3_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_3_text_shadow_blur_strength_tablet=”1px” header_4_text_shadow_horizontal_length=”header_4_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_4_text_shadow_horizontal_length_tablet=”0px” header_4_text_shadow_vertical_length=”header_4_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_4_text_shadow_vertical_length_tablet=”0px” header_4_text_shadow_blur_strength=”header_4_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_4_text_shadow_blur_strength_tablet=”1px” header_5_text_shadow_horizontal_length=”header_5_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_5_text_shadow_horizontal_length_tablet=”0px” header_5_text_shadow_vertical_length=”header_5_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_5_text_shadow_vertical_length_tablet=”0px” header_5_text_shadow_blur_strength=”header_5_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_5_text_shadow_blur_strength_tablet=”1px” header_6_text_shadow_horizontal_length=”header_6_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_6_text_shadow_horizontal_length_tablet=”0px” header_6_text_shadow_vertical_length=”header_6_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_6_text_shadow_vertical_length_tablet=”0px” header_6_text_shadow_blur_strength=”header_6_text_shadow_style,%91object Object%93″ header_6_text_shadow_blur_strength_tablet=”1px” box_shadow_horizontal_tablet=”0px” box_shadow_vertical_tablet=”0px” box_shadow_blur_tablet=”40px” box_shadow_spread_tablet=”0px” z_index_tablet=”500″]
This macroeconomic report is prepared based on eleven month’s data of FY 2021/22 published by NRB. The key macro-economic indicators and variables are highlighted in the table below and explained in further section :
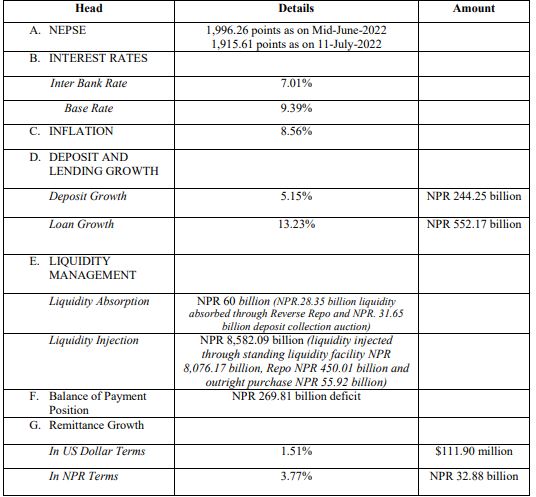
A. NEPSE and Ratio of Market Cap to GDP
The NEPSE index at Mid-June 2022 decline by -34.03% to close at 1,996.26 points, compared to 3,025.83 points in the same period last year. The Market capitalization of NEPSE as well decreased from NPR 4,216 billion in Mid-June 2021 to NPR 2,844.11 billion in Mid-June 2022.
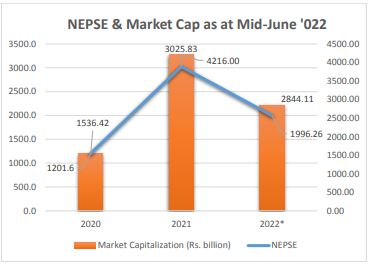
On the other hand, the ratio of market capitalization of NEPSE to GDP at Mid-June 2022 has decreased to 58.62% compared to 98.57% in the last year during the same review period.
B. INTEREST RATES
To evaluate the current scenario of interest rate in the economy, interbank rate and base rate of commercial banks are taken into consideration.
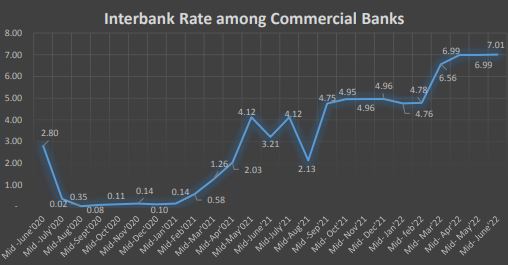
Interbank Rate
The interbank rate of commercial banks had decreased to 0.02% in Mid-Aug,2020 which has been gradually rising since then and has reached to 7.01% in Mid-June 2022 indicating tightening of liquidity in the banking system. The interbank rate during the same period a year ago stood at 3.21%.
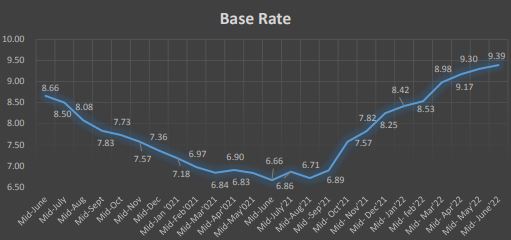
Base Rate
The base rate of commercial banks stands at 9.39% in Mid-June 2022 compared to 6.66% a year ago. This has set the weighted average lending rate at 11.54%. On the other hand, the weighted average deposit rate stands at 7.34%. Such rates were 8.46% and 4.72% respectively in the corresponding month of the previous year.
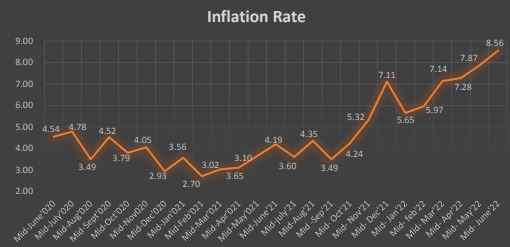
C. INFLATION RATE
The consumer price inflation which was 4.19% a year ago which has increased to 8.56% in Mid-June 2022. This is the highest increase in CPI index in past five years. Food and beverage inflation stood at 7.43 percent whereas non-food and service inflation stood at 9.44 percent in the review month. The average monthly y-o-y inflation for 11 months was 6.09 percent. The prices of ghee & oil, milk products & eggs, tobacco products, alcoholic drinks and pulses & legumes sub-categories rose by 22.60 percent, 11.22 percent, 9.70 percent, 9.68 percent and 9.13 percent respectively on y-o-y basis.
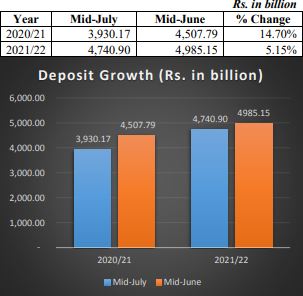
D. DEPOSIT AND LENDING GROWTH
Deposit Growth: The deposits of BFI’s as at Mid-June 2022 increased by 5.15% to NPR 4,985.15 billion, compared to NPR 4,740.90 billion in Mid-July 2021. The share of demand, saving, and fixed deposits in total deposits stands at 8.8 percent, 27.1 percent and 57.1 percent respectively in mid-June 2022. Such shares were 8.6 percent, 34.3 percent and 48.5 and 57.1 percent respectively in mid-June 2022.
Credit Growth: The credit disbursement of BFI’s as at Mid-June 2022 increased to NPR. 4,724.95 billion by 13.23%, compared to NPR 4,172.78 billion in Mid-July 2021. The growth during the same period last year was 25.39%. Outstanding loan of BFIs to the agriculture sector increased 20.1 percent, industrial production sector 9.6 percent, transportation, communication and public sector 12.6 percent, wholesale and retail sector 14.6 percent and service industry sector 5 percent in the review period.
In the review period, term loan extended by BFIs increased 22.7 percent, overdraft 12.6 percent, demand and other working capital loan 17.9 percent, real estate loan (including residential personal home loan) 16.8 percent and hire purchase loan 2.5 percent while that of trust receipt (import) loan decreased 53.8 percent and margin nature loan 17.6 percent
E. LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT
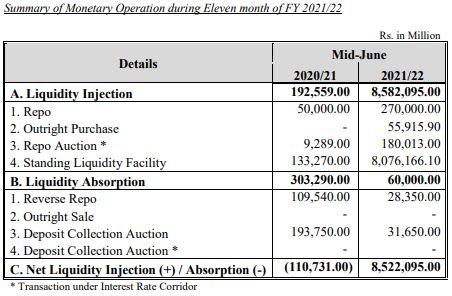
In the review period, NRB mopped up Rs.60 billion liquidity of which Rs.28.35 billion was through reverse repo auction and Rs.31.65 billion through deposit collection auction. In the corresponding period of the previous year, NRB mopped Rs.303.29 billion liquidity of which Rs.109.54 billion was through reverse repo and Rs. 193.75 billion through deposit collection auction.
In the review period, NRB injected Rs.8,582.09 billion liquidity of which Rs. 450.01 billion was through repo, Rs.55.92 billion through outright purchase and Rs.8,076.16 billion through standing liquidity facility. The NRB purchased Indian currency (INR) equivalent to Rs.529.74 billion through the sale of USD 4.40 billion in the review period. INR equivalent to Rs.489.98 billion was purchased through the sale of USD 4.16 billion in the corresponding period of previous year.
F. FISCAL SITUATION
Fiscal Deficit/Surplus
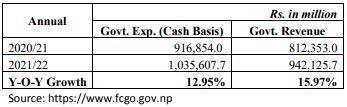
In the first eleven months of 2021/22, total revenue collected by the government till Mid-June 2022 is Rs.942.12 billion which is 15.97% higher compared with the corresponding month of the previous fiscal year. The total expenditure of the government till Mid-June 2022 is Rs.1,035.60 billion which is 12.95% higher than that of the expenditure on the corresponding month of previous fiscal year.
G. BALANCE OF PAYMENT POSITION
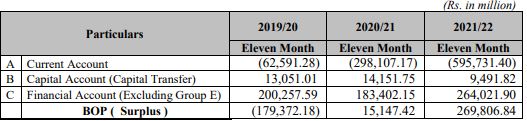
The country’s BOP position is at deficit in the first eleven month of FY 2021/22 by NPR 269.81 billion compared to a surplus of NPR 15.14 billion during the same period last year. On the other hand, the current account remained at a deficit of Rs.595.73 billion in the review period compared to a deficit of Rs.298.10 billion in the same period of the previous year.
In the review period, capital transfer decreased 32.9 percent to Rs.9.49 billion and net foreign direct investment (FDI) increased 7.1 percent to Rs.17.35 billion. In the same period of the previous year, capital transfer and net FDI amounted to Rs.14.15 billion and Rs.16.20 billion respectively.
WORKERS’ REMITTANCE
The workers’ remittance growth rate is subject to different terms of US Dollar and Nepalese Currency based on exchange rate of NPR with US Dollar. Hence, the workers’ remittance growth in terms of US Dollar and NPR has been presented below:
Remittance in Dollar Terms
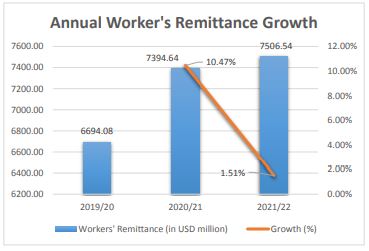
In US Dollar terms, the workers’ remittance increased by 1.51% to $7,506.54 million during the first eleven months in FY 2021/22 compared to an increase of 10.47% during the same period in FY 2020/21.
Remittance in NPR terms
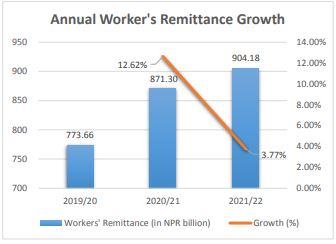
On the other hand, in NPR terms, the workers’ remittance increased by 3.77% to NPR 904.18 billion during the first eleven months in FY 2021/22 compared to a rise of 12.62% during the same period in FY 2020/21.
Number of Nepali workers (institutional and individual-new and legalized) taking approval for foreign employment increased significantly to 313,367 in the review period. It had decreased 68 percent in the same period of the previous year. The number of Nepali workers (Renew entry) taking approval for foreign employment increased 208.3 percent to 259,091 in the review period. It had decreased 52.1 percent in the same period of the previous year. Net transfer increased 3.6 percent to Rs.1006.07 billion in the review period. Such a transfer had increased 11.5 percent in the same period of the previous year.
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]



